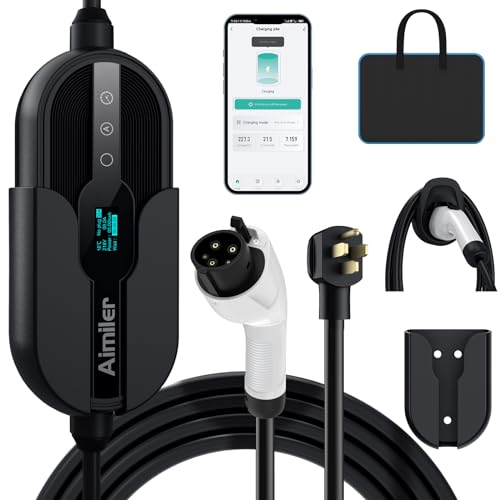
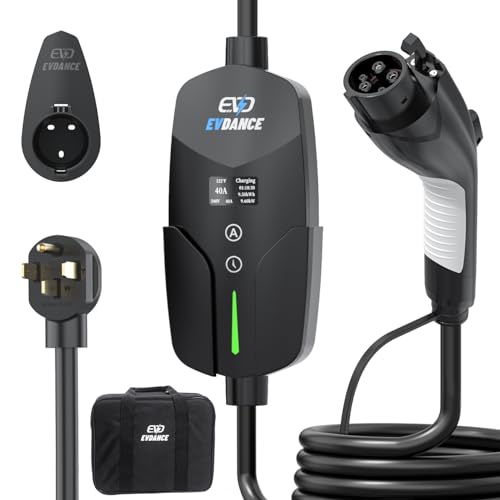
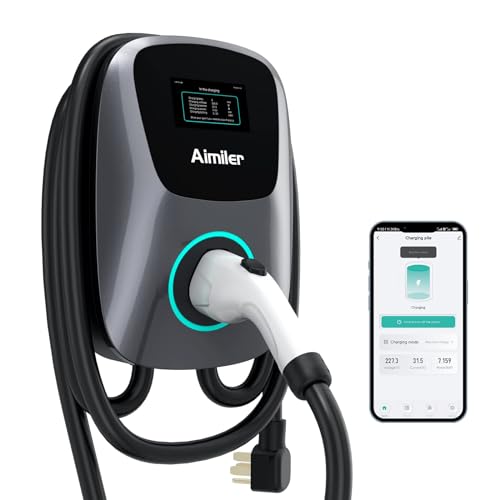
With the increasing popularity of electric vehicles (EVs), the demand for efficient and accessible charging infrastructure has never been higher. Electric vehicle chargers play a crucial role in supporting the transition to sustainable transportation by providing EV owners with convenient and reliable ways to power up their vehicles. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore everything you need to know about electric vehicle chargers, from the different types available to the factors to consider when choosing one for your needs.
Types of Electric Vehicle Chargers
What is Level 1 Charging?
Level 1 charging is the slowest form of EV charging available, utilizing a standard 120-volt AC outlet, which is the typical household outlet in the United States. This type of charging is often referred to as "trickle charging" due to its relatively slow pace. A Level 1 charger usually comes with the vehicle and doesn't require any special installation, making it the most straightforward and cost-effective charging option for EV owners.
Features of Level 1 Chargers
Voltage and Power: Operating on a 120V AC outlet, Level 1 chargers typically deliver about 1.4 kW to 2 kW of power. This translates to adding about 4 to 5 miles of range per hour of charging, although this can vary based on the vehicle's efficiency.
Ease of Use: Since Level 1 charging can be done using standard household outlets, it requires no special installation. Users simply plug the charger into the outlet and connect it to their vehicle.
Portability: Level 1 chargers are generally portable, allowing users to charge their EVs wherever they have access to a 120V outlet.
Benefits of Level 1 Charging
Accessibility: The universal availability of 120V outlets makes Level 1 charging the most accessible form of EV charging.
Cost-Effectiveness: With no need for special installation, Level 1 charging is an affordable option, especially for new EV owners or those who drive shorter distances.
Convenience for Overnight Charging: Level 1 charging is ideal for overnight use, as it allows the vehicle to be charged at home, ready for use the next day.
Limitations of Level 1 Charging
Slow Charging Speed: The primary drawback of Level 1 charging is its slow pace. It is not suitable for quick top-ups or for vehicles with large batteries if they need to be fully charged in a short amount of time.
Limited Practicality for Long-Distance Travel: For EV owners who frequently drive long distances, relying solely on Level 1 charging can be impractical due to the extended charging times required.
Who Should Use Level 1 Charging?
Level 1 charging is particularly well-suited for:
City Dwellers and Short Commuters: Those who drive short distances and can fully recharge their vehicle overnight.
Second Vehicle Owners: Households using the EV as a secondary vehicle for short trips or commutes.
Emergency and Backup Charging: Level 1 chargers are excellent as a backup option for any EV owner, providing peace of mind in case other charging options are unavailable.
The Role of Level 1 Charging in the EV Ecosystem
While Level 1 charging may not meet the needs of all EV owners, it plays a critical role in the broader EV charging ecosystem. It provides a universally accessible entry point into EV ownership, requiring no additional infrastructure or investment beyond the vehicle itself. As the EV market continues to evolve, advancements in battery technology and vehicle efficiency may further enhance the utility of Level 1 charging for a broader range of users.
Level 1 electric vehicle chargers offer a simple, accessible, and cost-effective solution for many EV owners, especially those with modest daily driving needs. While not the fastest charging option, Level 1 charging is an important part of the EV infrastructure, ensuring that all EV owners have a reliable method of charging their vehicles. As the transition to electric mobility progresses, understanding and utilizing Level 1 charging will remain a fundamental aspect of EV ownership for many drivers.
What is Level 2 Charging?
Level 2 charging utilizes a 240-volt AC power source, which is significantly more powerful than the 120-volt AC power used by Level 1 chargers. This increase in voltage allows Level 2 chargers to provide a much quicker charging experience, making them ideal for both home and public charging stations.
Features of Level 2 Chargers
Voltage and Power: Operating on a 240V AC supply, Level 2 chargers typically deliver between 3.3 kW to 19.2 kW of power. This enables them to add about 12 to 80 miles of range per hour of charging, depending on the charger's capacity and the vehicle's acceptance rate.
Charging Time: Compared to Level 1 chargers, Level 2 chargers can significantly reduce charging time, fully charging most EVs in just a few hours.
Equipment and Installation: Level 2 charging stations require the installation of a dedicated 240V circuit and the charging unit itself. Many units are designed for both indoor and outdoor use, offering flexibility for installation at homes, workplaces, and public locations.
Benefits of Level 2 Charging
Efficiency and Speed: The most notable advantage of Level 2 charging is its efficiency, providing a faster charging solution that can conveniently fit into daily routines.
Increased Accessibility: With the growing network of public Level 2 charging stations, EV owners can easily find charging options while on the go, making longer trips more feasible.
Enhanced Convenience: For home installations, Level 2 chargers offer the convenience of "refueling" your vehicle overnight or even just in a few hours, ensuring it's always ready for use.
Smart Charging Features: Many Level 2 chargers come equipped with smart features such as scheduling, power management, and remote access via smartphone apps, enhancing the user experience.
Installation Considerations
Installing a Level 2 charging station typically involves some upfront investment and planning. Homeowners may need to upgrade their electrical service to accommodate the 240V requirement and should consult with a professional electrician to ensure compliance with local building codes and safety standards. Additionally, many governments and utilities offer incentives and rebates to offset the installation costs, making it more affordable for EV owners.
The Role of Level 2 Charging in EV Adoption
Level 2 charging plays a crucial role in facilitating the widespread adoption of electric vehicles. By providing a more practical and efficient charging solution, Level 2 chargers help to alleviate one of the primary concerns potential EV buyers have: range anxiety. The availability of Level 2 charging at home and in public spaces ensures that EV owners can enjoy the benefits of electric driving without significant compromises to their lifestyle or mobility.
Level 2 electric vehicle chargers represent a significant step forward in EV charging technology, offering a balance of speed, convenience, and accessibility. As the EV market continues to grow, the demand for Level 2 charging solutions will undoubtedly increase, both in public infrastructure and private homes. Understanding the features, benefits, and considerations of Level 2 charging is essential for current and prospective EV owners, as it highlights the advancements in EV technology that make electric driving more accessible and enjoyable for everyone.
The Evolution of Electric Vehicle Charging: Unveiling DC Fast Chargers (Level 3 Chargers)
As electric vehicles (EVs) gain popularity, the demand for quicker, more efficient charging solutions has led to significant advancements in charging technology. Among these, Direct Current (DC) Fast Chargers, often referred to as Level 3 Chargers, stand out as the pinnacle of rapid charging technology. This article explores the intricacies of DC Fast Charging, its benefits, operational principles, and the pivotal role it plays in the adoption and convenience of EVs.
Understanding DC Fast Charging
DC Fast Charging represents a leap forward in EV technology, offering the fastest charging speeds currently available. Unlike Level 1 and Level 2 chargers, which use Alternating Current (AC), DC Fast Chargers supply Direct Current (DC) directly to the EV's battery, significantly reducing charging times.
Key Features of DC Fast Chargers
Power Output: DC Fast Chargers typically operate at a power range between 50 kW and 350 kW, with some newer models pushing the envelope further. This high power output allows these chargers to add 60 to 100 miles of range in just 20 minutes of charging for many vehicles, a feat that is impossible for Level 1 or Level 2 chargers.
Charging Time: Depending on the battery's capacity and the charger's power output, DC Fast Chargers can recharge an EV's battery from 20% to 80% in approximately 20 to 40 minutes, making them ideal for quick stops during long trips.
Connectors: DC Fast Chargers use specific connectors, such as the Combined Charging System (CCS), CHAdeMO, or Tesla’s proprietary connector, to accommodate different EV models and standards.
Benefits of DC Fast Charging
Convenience on Long Journeys: DC Fast Charging stations are often located along highways and in urban areas, providing EV drivers with the convenience of quick recharging during long-distance travel.
Reduced Downtime: For commercial EV fleets, including buses and delivery vehicles, DC Fast Charging means reduced downtime and higher operational efficiency.
Encourages EV Adoption: By alleviating range anxiety and reducing charging wait times, DC Fast Charging plays a crucial role in encouraging the adoption of electric vehicles among the general public.
Operational Considerations
Despite their advantages, DC Fast Chargers come with certain considerations. The cost of installing and operating DC Fast Charging stations is significantly higher than that of Level 1 or Level 2 chargers, due to the advanced technology and higher power requirements. Additionally, not all EVs are equipped to handle the fastest charging speeds, and frequent use of DC Fast Charging can affect battery health over time, although modern EVs are designed to minimize this impact.
The Role of DC Fast Charging in EV Infrastructure
The expansion of DC Fast Charging infrastructure is key to the widespread adoption of electric vehicles. Governments and private companies worldwide are investing in the deployment of DC Fast Charging stations to create a network that can support the growing number of EVs on the road. This infrastructure is crucial for making EVs a viable option for more drivers, especially those who regularly undertake long-distance travel.
DC Fast Chargers represent the cutting edge of EV charging technology, offering speed and efficiency far beyond what Level 1 and Level 2 chargers can provide. As the EV market continues to evolve, the importance of DC Fast Charging in supporting the transition to electric mobility cannot be overstated. By reducing charging times and making electric vehicles more convenient for long-distance travel, DC Fast Charging is set to play a pivotal role in the future of transportation, driving forward the adoption of clean, sustainable electric vehicles for all.
General Considerations When Buying An EV Charger
1. Charging Level
Understanding the different levels of EV charging is paramount in making the right choice:
Level 1 Chargers are the most basic, using a standard 120-volt AC outlet. While they don't require special installation, they offer slow charging, typically suited for overnight use or for those with minimal daily driving distances.
Level 2 Chargers operate on 240-volt AC power, significantly reducing charging times compared to Level 1 chargers. They require a dedicated circuit and professional installation but are ideal for home use and can fully charge an EV overnight.
DC Fast Chargers (Level 3 Chargers) offer the fastest charging speeds by delivering direct current (DC) directly to the vehicle's battery. These are primarily found in commercial and public charging stations due to their high cost and power requirements.
2. Charging Speed
Charging speed is a crucial factor, influencing how quickly your EV's battery can be recharged. This is determined by the charger's power output, measured in kilowatts (kW). Higher kW chargers can deliver more power and thus charge your vehicle faster. Consider your vehicle's maximum charging rate and choose a charger that matches or exceeds this rate to ensure optimal charging efficiency.
3. Installation Requirements
Before choosing an EV charger, consider the installation process and requirements. Level 2 chargers, for example, often require professional installation, a dedicated 240V circuit, and possibly an upgrade to your home's electrical system. Evaluate the feasibility and cost of installation in your home or desired location to avoid unexpected expenses or complications.
4. Portability and Location
Determine whether you need a fixed or portable charger. Fixed chargers are mounted in a permanent location, offering convenience and security, especially for home charging. Portable chargers, on the other hand, provide flexibility and are ideal for individuals who travel frequently or do not have a fixed parking space.
5. Smart Features
Many modern EV chargers come equipped with smart features that enhance user experience and functionality. These may include:
Wi-Fi or Bluetooth Connectivity: Allows you to monitor and control your charger remotely through a smartphone app.
Scheduling: Enables you to set charging times to take advantage of off-peak electricity rates, reducing costs.
Energy Management: Some chargers can adjust the charging rate based on your home's current energy usage to prevent overloading your electrical system.
6. Cost
The cost of an EV charger encompasses not only the purchase price but also installation costs and potential upgrades to your electrical system. While higher-end models with advanced features and faster charging speeds may be more expensive, they can offer greater convenience and efficiency. Consider available rebates, tax incentives, and utility programs that may offset some of these costs.
7. Compatibility
Ensure the charger you choose is compatible with your EV. This includes the type of connector used and whether the charger is compatible with your vehicle's charging specifications. Most new EVs use a standard connector type such as CCS or CHAdeMO for DC fast charging, but it's important to verify this before making a purchase.
8. Safety and Certification
Safety should never be overlooked when choosing an EV charger. Look for chargers that are certified by recognized standards organizations, such as Underwriters Laboratories (UL) in the United States. These certifications ensure that the charger has passed rigorous safety tests and meets high-quality standards.
9. Manufacturer and Warranty
Consider the reputation of the charger manufacturer and the warranty provided. A reputable manufacturer will likely offer a more reliable, durable product and better customer support. A comprehensive warranty can also provide peace of mind, covering potential defects or issues over the life of the charger.
Choosing the right electric vehicle charger is a multifaceted decision that requires careful consideration of several key factors. By assessing your specific needs, preferences, and circumstances, you can select a charger that offers the right balance of speed, convenience, and cost-effectiveness. As the EV market and charging technologies continue to evolve, staying informed and adaptable will ensure that your charging solution remains compatible with your lifestyle and the broader ecosystem of electric mobility.
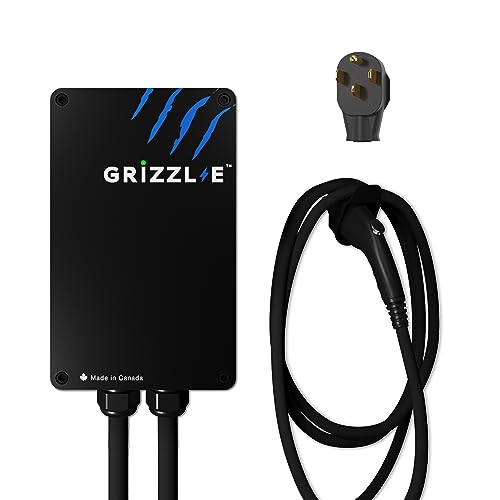
Grizzl-E Level 2 Fast EV Charger, Classic Black
Effortlessly charge your electric vehicle with the sleek and reliable Grizzl-E Level 2 Fast EV Charger in timeless Classic Black
Product information
$399.00 $349.99
Product Review Score
4.42 out of 5 stars
67 reviews